When it comes to optimizing production, picking the right Homogenizer Vessel is super important, especially for industries that rely on high-pressure homogenization and microfluidization. I recently came across a market report from Grand View Research, and guess what? It forecasts the global market for homogenizers to hit around USD 1.12 billion by 2027. That’s mainly because there's growing demand from fields like pharma, cosmetics, and food production.
 CAS PETER (HANGZHOU) NANOTECHNOLOGY CO., LTD is really leading the way here—focusing on research and sales of high-pressure homogenizers and microfluidizers that fit a bunch of different industrial needs. As companies aim to bump up their product quality and keep things consistent, getting a good grip on the different types of Homogenizer Vessels is pretty much essential. You want to make sure they match your technical requirements and overall production goals. In this blog, I’ll break down the different kinds of Homogenizer Vessels out there so you can make smarter, more informed choices based on what your specific production process needs.
CAS PETER (HANGZHOU) NANOTECHNOLOGY CO., LTD is really leading the way here—focusing on research and sales of high-pressure homogenizers and microfluidizers that fit a bunch of different industrial needs. As companies aim to bump up their product quality and keep things consistent, getting a good grip on the different types of Homogenizer Vessels is pretty much essential. You want to make sure they match your technical requirements and overall production goals. In this blog, I’ll break down the different kinds of Homogenizer Vessels out there so you can make smarter, more informed choices based on what your specific production process needs.
When it comes to mixing liquids in industrial settings, picking the right type of homogenizer vessel is super important if you want to boost production and get consistent results. There are a few different kinds of homogenizer vessels out there, each built for specific processing needs. For example, high-pressure homogenizers work by forcing the liquid through a tiny gap at really high pressure, creating kind of a turbulent environment that blows apart particles and makes everything uniform. They're especially handy in industries like dairy, pharma, and cosmetics—anywhere you really need a stable emulsion.
On the flip side, batch homogenizers are more suited for smaller runs. They allow for more controlled mixing and often take less time, which makes them perfect for R&D or companies working with limited quantities. Then there’s the inline homogenizer—a popular choice for bigger operations. It processes the mixture continuously as it flows through the system, so you get a steady output without stopping. That’s great if you’re looking for efficiency and consistency. Basically, understanding these options can really help businesses pick the right vessel that matches their production needs without a lot of headaches.
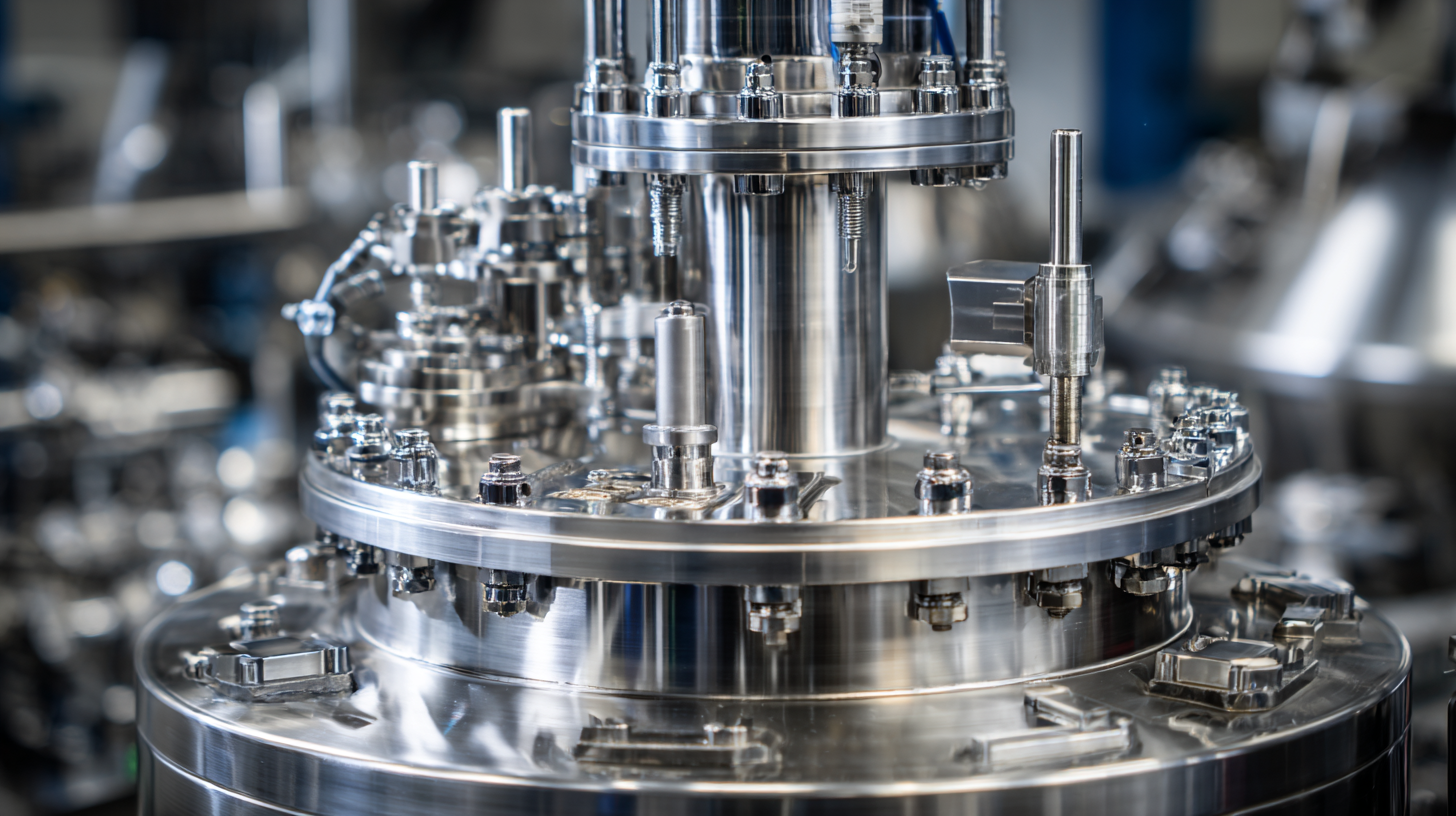

When you're picking out a homogenizer vessel, it’s pretty important to get a good grip on the key features that’ll work best for your production needs. First off, think about what material the vessel is made of — it really affects how tough it is and what kinds of products you can process. Stainless steel is a common go-to because it resists corrosion and’s super easy to clean, making it a solid choice for food or pharma stuff. That said, if you're working with smaller batches or need to see what's going on inside, glass vessels might be a better fit.
Here's a little tip: Make sure to check the vessel’s capacity against your typical production volume. If it’s too big, you might be wasting resources; too small, and you'll probably end up wasting time figuring out how to get everything processed efficiently.
Another thing to keep in mind is the design of the vessel. You’ll want something that's easy to maintain and clean — things like detachable lids or smooth internal surfaces make life easier. Oh, and don’t forget about the mixing technology inside — it really makes a difference in how well the homogenization works.
And here’s another tip: Energy consumption matters more than you might think. Choosing an energy-efficient vessel can save you some serious cash in the long run. By evaluating all these features, you’ll be better equipped to pick the right homogenizer vessel that matches what you actually need for production.
| Type | Capacity (Liters) | Pressure Rating (Bar) | Material | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Batch Homogenizer | 50 | 200 | Stainless Steel | Food, Pharmaceutical |
| Inline Homogenizer | 120 | 300 | Hastelloy | Chemical Processing |
| Continuous Homogenizer | 200 | 250 | Carbon Steel | Cosmetic, Chemical |
| Ultrasonic Homogenizer | 10 | N/A | Aluminum | Laboratory, Small Scale |
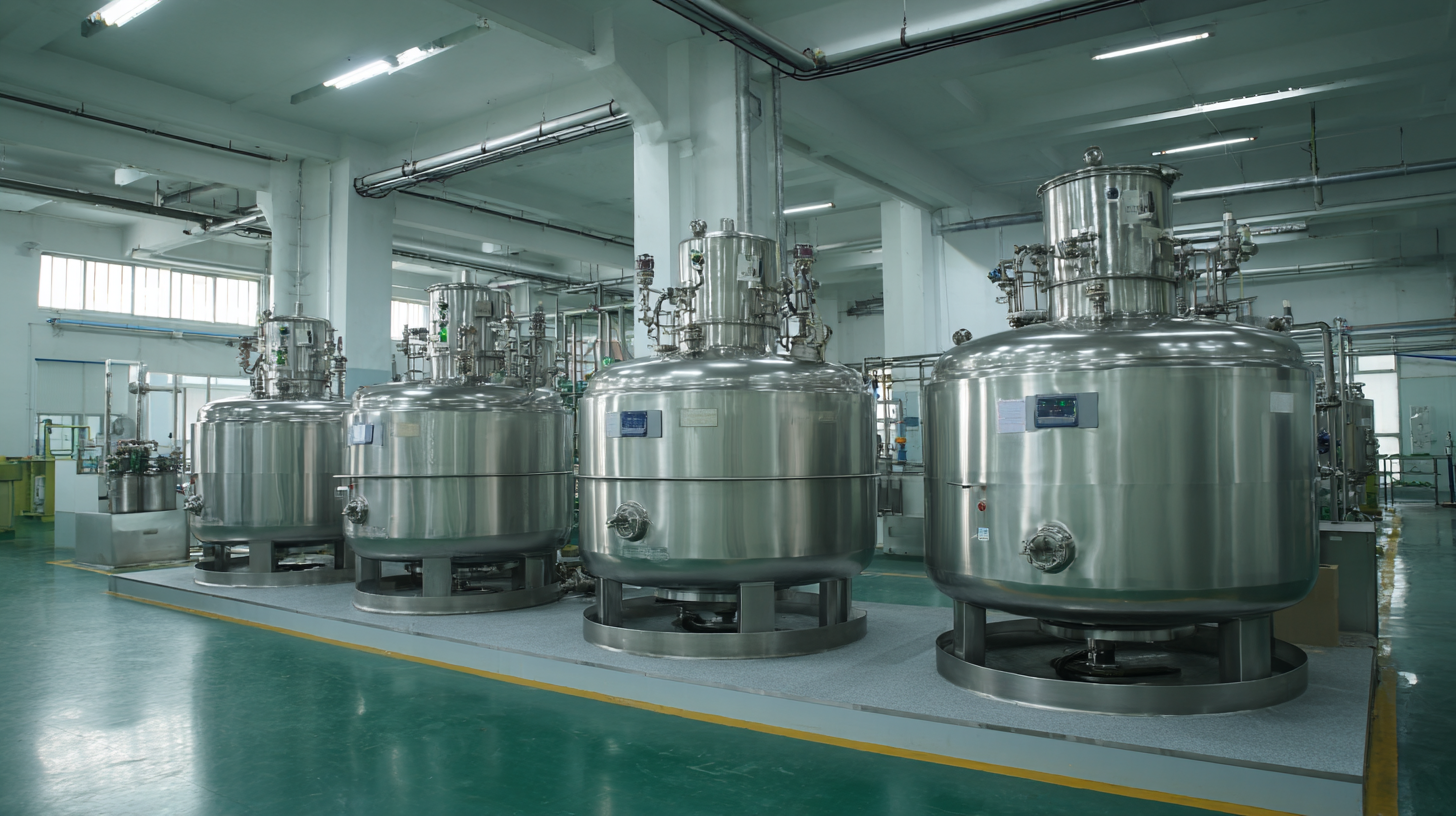
When we're talking about homogenization in production processes, picking between
batch and
continuous homogenizer tanks is a pretty big deal.
 Batch homogenizers are great if you're working on
smaller runs—they give you the kind of flexibility to switch up formulas quickly, which is pretty handy.
Plus, they let you control the process quite precisely, making them perfect for products that need just the right
texture or consistency. This kind of adaptability often results in a better final product, especially in fields like
pharma or cosmetics, where getting the formulation spot-on really matters.
Batch homogenizers are great if you're working on
smaller runs—they give you the kind of flexibility to switch up formulas quickly, which is pretty handy.
Plus, they let you control the process quite precisely, making them perfect for products that need just the right
texture or consistency. This kind of adaptability often results in a better final product, especially in fields like
pharma or cosmetics, where getting the formulation spot-on really matters.
On the flip side,
continuous homogenizers are all about high-volume stuff.
They work by feeding materials nonstop, boosting overall throughput and cutting down on downtime for cleaning or switching
batches. That makes them a no-brainer for industries like food and beverages,
where producing huge amounts of a uniform product quickly and reliably is key. But, here’s the catch—they’re a bit less flexible.
Changing up formulations can require more tweaks and adjustments to the system, which isn't as straightforward.
So, at the end of the day, you really gotta think about what your production needs are and what kind of products you’re working with.
Making the right choice between batch and continuous homogenization depends heavily on your specific situation
and what’s more important—flexibility or efficiency.
When you're choosing the right homogenizer vessel for your production setup, the material you pick really makes a big difference in both efficiency and the quality of your final product. Common options—like stainless steel, glass, and plastic—each come with their own perks and downsides. For example, stainless steel is pretty much the go-to because it’s tough, resistant to rust, and handles high-pressure processes really well. The catch? It can be a bit pricey, and it’s heavier, which might mean higher costs when it comes to moving and installing it.
Then there’s glass. If you need something with high visibility and excellent chemical resistance, glass vessels are a solid choice—they're easy to clean and won't react with your product, keeping things pure. But, heads up—glassy stuff is fragile, so if you’re running at high speeds or dealing with rough handling, it could be risky.
And don’t forget about plastic. It’s lightweight and usually cheaper, so it’s great if you’re watching your budget or need something easy to move around. But, keep in mind, it probably won’t last as long or handle the same pressures as metal or glass. So, really, it’s all about weighing your specific production needs and understanding what each material brings to the table. That way, you can pick a vessel that works best for you, without any surprises down the line.
This bar chart compares the durability of various homogenizer vessel materials on a scale of 1 to 10. Stainless steel ranks highest in durability, followed by ceramic, while polypropylene has the lowest rating.
When you're trying to pick the right homogenizer vessel for your production process, it’s really important to think about your specific needs and the applications you're dealing with. There are different types of vessels out there, each designed to handle particular materials and deliver the best results. For example, bead mills are great if you need to break particles down effectively and get a good dispersion. Their design makes it easy for the beads to interact with the material, which helps with thorough mixing.
On the flip side, vacuum mixer homogenizers are a must-have if your process requires working under a full vacuum or internal pressure. These vessels not only improve mixing but also give you the option to heat or cool your materials, so you can control the environment really precisely. As techniques in cell biology keep advancing, more folks are looking for homogenizers that are especially good at breaking open cells. Vessels made for this purpose do a great job of disrupting cell membranes without damaging delicate cellular parts, which means you can get a higher yield and keep your samples intact.
Basically, choosing the right vessel based on what you're trying to do is key to getting the best results in your production. Don’t just pick something random—think about the specific application and go for what’s most suitable to make sure everything runs smoothly.
When you're choosing a homogenizer vessel for your production setup, it's pretty important to think about how cost-effective each type is. These vessels come in all sorts of materials and designs, and each one offers different perks that can affect both your initial spend and what you’ll be paying over the long run. For example, stainless steel is super popular because it’s tough and resists corrosion, but it does tend to be pricier upfront—something smaller operations might hesitate to invest in. On the other hand, options like polymer or glass vessels might be easier on the wallet, but they might not handle high pressure or extreme temps as well as stainless steel does.
Plus, the type you pick can really impact your maintenance costs down the line. Stainless steel vessels, while more expensive at the start, typically last longer and don't need replacing as often, which can save you money in the long run. Buying quality homogenizer vessels isn’t just about saving now; it can boost efficiency, cut down on downtime, and help you get more done overall. So, taking a close look at what makes each option cost-effective is key—this way, you can make smarter decisions that fit your budget but still keep your production running smoothly.
: Stainless steel is commonly used due to its durability and resistance to corrosion, making it ideal for high-pressure operations and applications in the food and pharmaceutical industries.
Glass vessels are preferred for their high visibility and chemical resistance. They do not react with products, ensuring purity, and are easy to clean.
Glass vessels are more fragile and can pose a risk in high-speed environments, making them less suitable for some applications.
It's important to evaluate the capacity in relation to production volume; a vessel too large may waste resources, while one too small can cause inefficiencies and increased processing times.
The vessel's design should allow for easy maintenance and cleaning, with features like detachable lids and smooth internal surfaces to facilitate these processes.
Opting for an energy-efficient vessel can significantly reduce operational costs over time, making it an important consideration for production efficiency.
Plastic vessels are lightweight and cost-effective, but they may not offer the same longevity or pressure resistance as stainless steel or glass options.
The type of mixing technology used can significantly affect the quality of the homogenization process, influencing the final product's consistency and characteristics.
It's essential to weigh the advantages and disadvantages of each material—stainless steel, glass, and plastic—to make an informed decision based on the specific demands of the production process.
When it comes to today’s production scene, picking the right Homogenizer Vessel is pretty much a big deal if you want those top-notch results across different applications. In this post, we’ll take a good look at the different types out there, pointing out what makes each one special and the perks they offer. We’ll cover everything from the differences between batch and continuous processes to how different materials can impact performance—so you can figure out what works best for your needs. Plus, we’ve included some specific tips based on different applications and broken down the costs, so you can make smarter, more informed choices.
Here at CAS PETER (HANGZHOU) NANOTECHNOLOGY CO., LTD, we’re passionate about pushing the boundaries of nanotech. Our goal is to ensure that our high-pressure homogenizers and microfluidizers aren’t just good on paper but actually meet the tough demands of real-world industry. By getting a handle on the ins and outs of Homogenizer Vessels, your business can really step up its production game and get the most out of what homogenization technology has to offer.







